Online Job Advertisements (OJA)
Introduction
Building on this initial work, Eurostat, in close collaboration with the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (Cedefop), set up in 2020 the Web Intelligence Hub (WIH) and launched a dedicated ESSnet for the setting up of the Web Intelligence Network (WIN) in 2021.
Through the WIH, statisticians can access data from millions of OJAs collected from diverse sources, including private job portals, public employment service portals, and recruitment agencies. OJA data is released to statisticians on the WIH's DataLab, on a quarterly basis.
Currently, Eurostat is using WIH OJA data to produce experimental statistics on on Demand on ICT specialists in OJA and Online Job Advertisement Rate (OJAR). Eurostat has also launched the Top & Trending skills app based on the WIH OJA data.
Cedefop's uses WIH OJA data to source Skills-OVATE that offers detailed information on the jobs and skills employers demand based on online job advertisements.
Methodology
The OJA data production system, developed initially by Cedefop and integrated into Eurostat's Web Intelligence Hub (WIH), is a multi-stage system for collecting, processing, and disseminating data from online job advertisements. Its primary goal is to extract from online job advertisements, information about the labor market, such as skill demand, employment trends, and qualification needs.
The OJA data production comprises several steps, each with its specific processes and outputs:
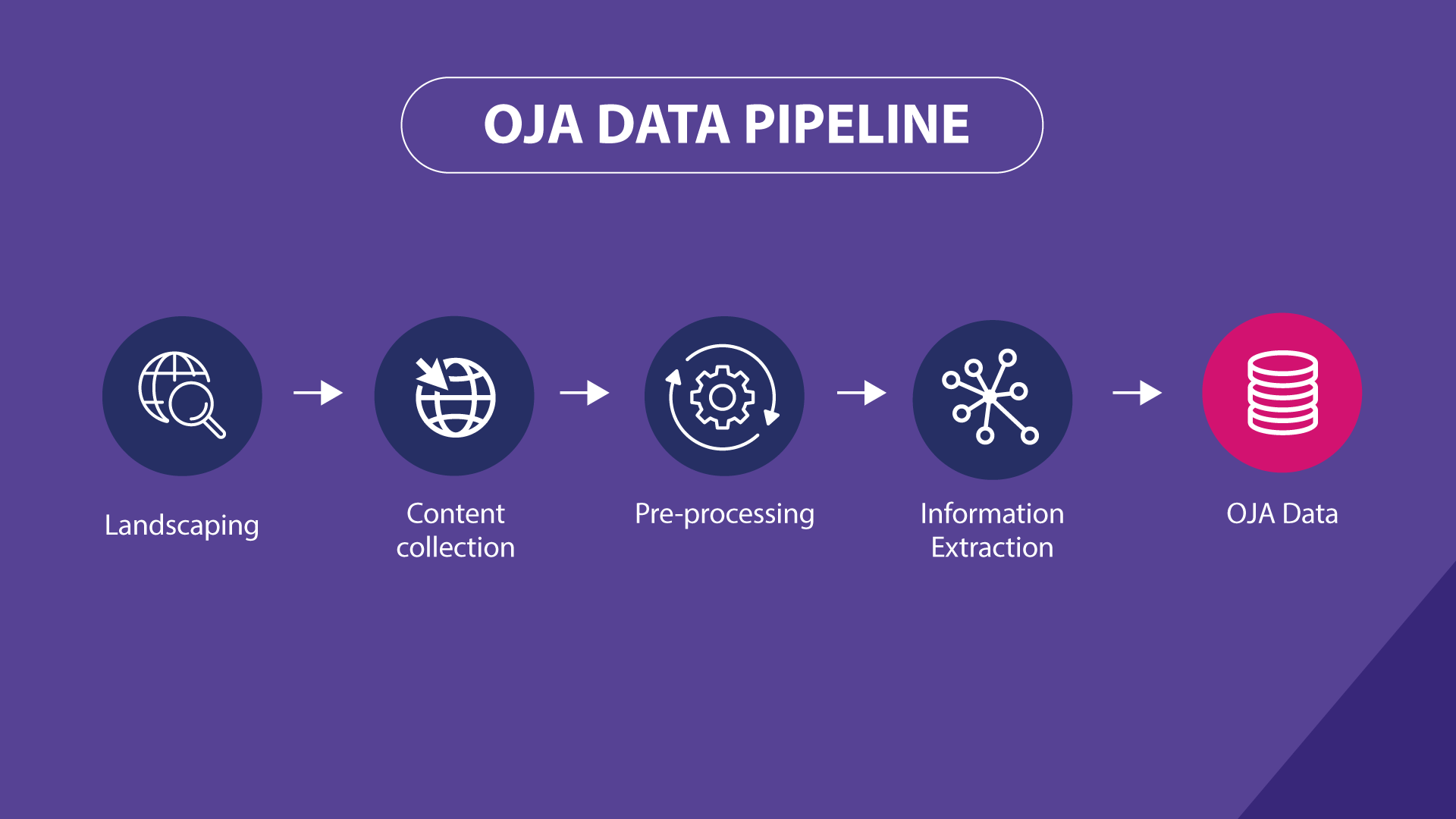
Landscaping
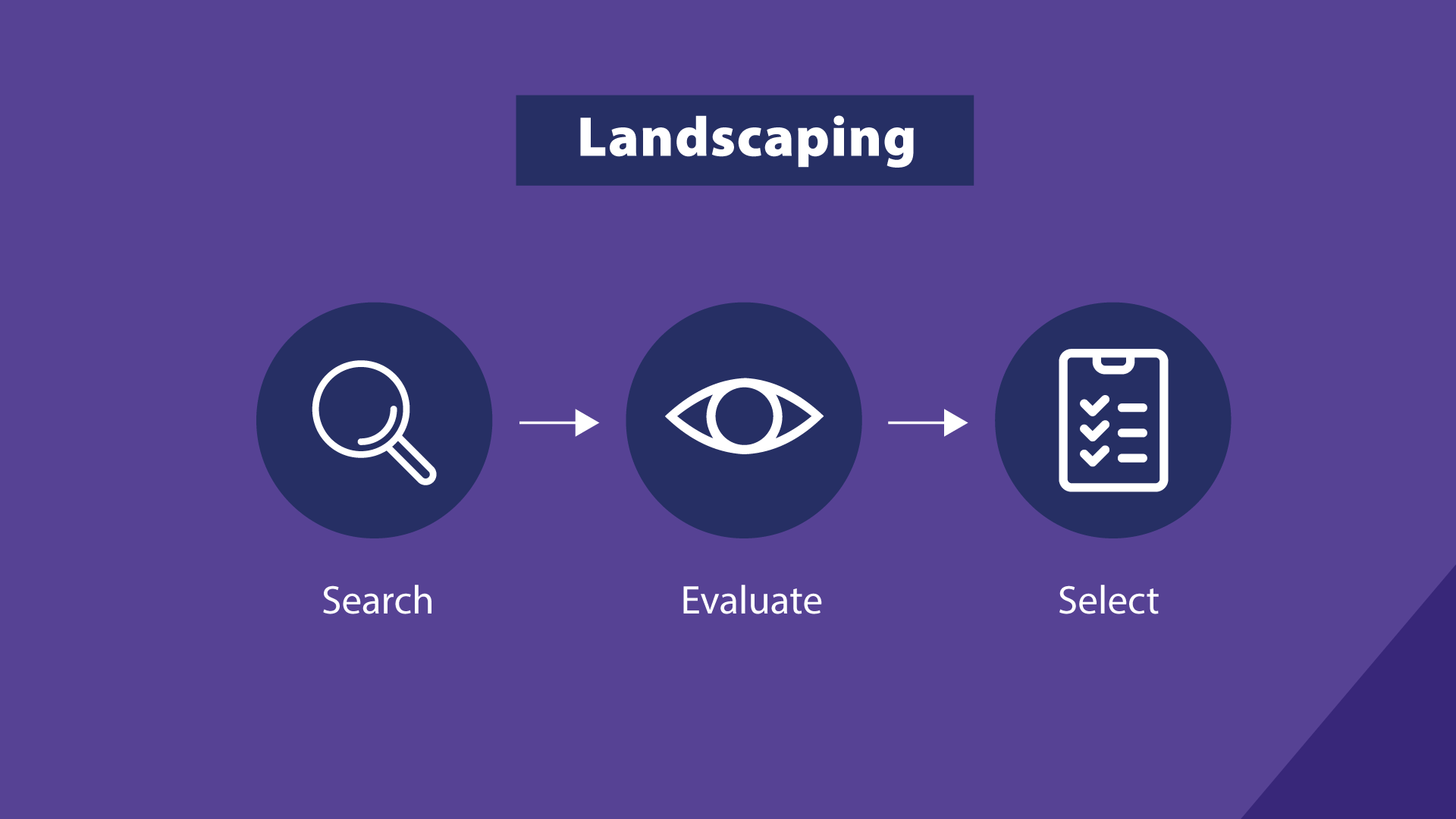
The landscaping has the purpose to make an exhaustive inventory of all OJA web sources under scope, assess their quality, and select the ones to be used for the collection of OJAs.
The first landscaping was conducted in 2017 by Cedefop, covering 27 EU Members-States plus the UK, establishing an initial set of relevant job portals. In 2021, a second landscaping was conducted by Eurostat, updating the sources for the initial countries and expanded coverage to include also the EFTA Member-States.
Both landscaping exercises were done with the support of labour market experts, one for each country. Experts used their own knowledge of the national labour markets and standardised search methods to identify a list, as complete as possible, of all the relevant job portals. Experts then assessed the characteristics of each job portal and the quality of their content. Using both quantitative and qualitative measures, such as popularity, stability, and coverage, sources were ranked based on their quality and the top ones selected for the collection of OJAs. More information on the second landscaping exercise can be found in the corresponding implementation report.
OJA collection
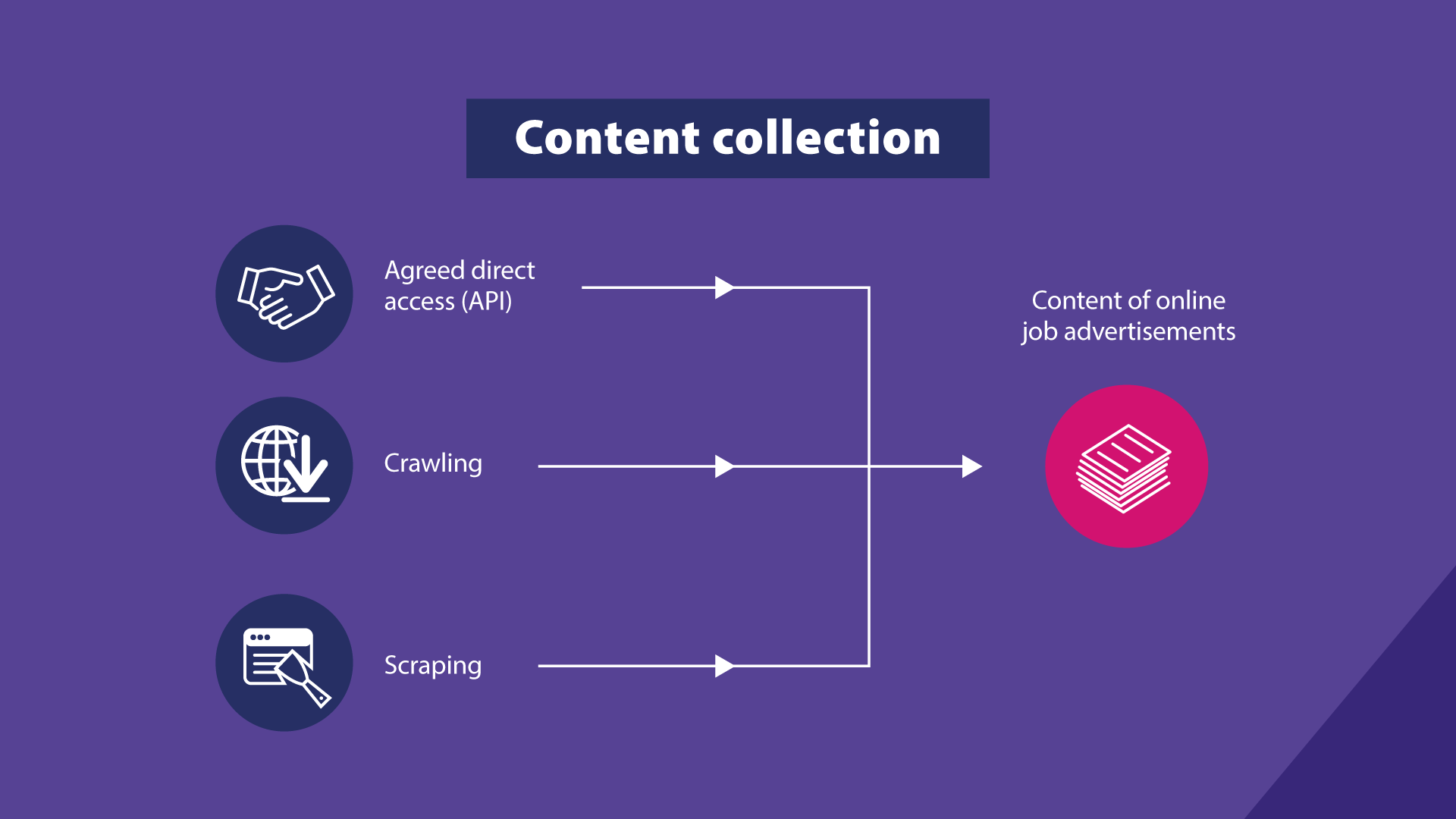
OJAs are collected from the selected job portals through three main methods:
- Scraping: This method extracts structured content from websites where information is organized by precise web field location.
- Crawling: This method uses a programmed bot to navigate portals and download the full content of web pages. As a result, it collects more irrelevant content compared to scraping.
- Direct API Access: This method enables content download directly from job portal databases, providing high-quality data, but requires formal agreements with website operators.
Pre-processing
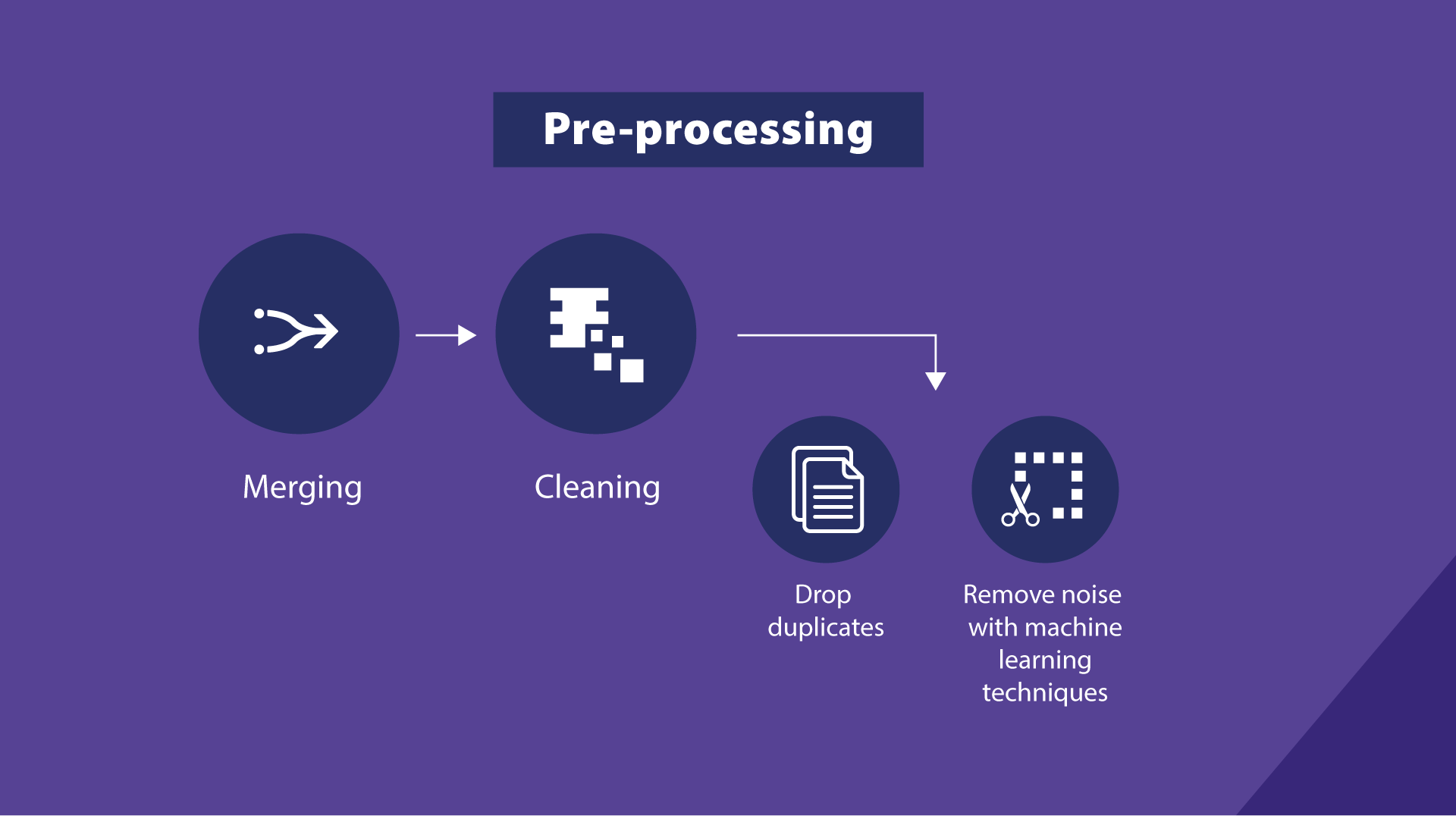 Collected OJA content is cleaned and prepared, including:
Collected OJA content is cleaned and prepared, including:
- Cleaning: Removal of noise and content not referring to job advertisements, such as portals general information pages.
- Deduplication: Advertisements identified as duplicates through job descriptions, location, and metadata, are clearly flagged.
- Merging: Combines information from duplicate advertisements posted on multiple portals.
Information Extraction
 Information is extracted from job advertisements using ontologies and machine learning models to structure the content by statistical variable and according to relevant statistical classifications. The process is conducted in each advertisement's original language.
Information is extracted from job advertisements using ontologies and machine learning models to structure the content by statistical variable and according to relevant statistical classifications. The process is conducted in each advertisement's original language.
- Ontologies: Classification is based on a pre-defined set of terms associated to each category of the classification used for each variable. The identification of the right term in the right place of the text then leads the job advertisement to be classified in the corresponding category.
- Machine Learning Models: Classification is based on a probabilistic model estimated with a set of examples (training data) previously classified by experts.
Quality
Due to the nature of online job advertisements, generated for the purpose of recruiting and not for statistical purposes, quality of the resulted data is a crucial concern. The OJA data production system employs a quality control process, which includes:
- Data Validation: Verification of data accuracy and consistency using validation rules and review by WIH statisticians.
- Quality Monitoring: Procedures to evaluate and improve data collection and classification algorithms, including the creation of a "gold standard" for evaluation and feedback.
Additional Considerations
Despite its comprehensive scope, the OJA data has limitations:
- Representativeness: Not all job openings are advertised online, and some job types are more likely to be advertised online than others, potentially leading to bias in the statistics if it not taken into account.
- Internet Penetration: The use of online job portals as a recruitment channel is different from country to country, influenced by internet penetration and the digital skills of the population, leading to more limited comparability.
- Classification Errors: Even with advanced algorithms, automated information extraction can contain errors.
- Ontology Limitations: Ontologies used to classify job advertisements may have errors or gaps.
The WIH OJA data production system is continuously evolving, with new features and improvements regularly added. Collaboration between Eurostat and Cedefop, within the WIH framework, contributes to high-quality data production for creating relevant labor market statistics and indicators across Europe.
Use of OJA data
OJA data in the WIH is available to the European Statistical System (ESS) members, National Statistical Institutes and other national statistical authorities of the EU and EFTA Member-States.
OJA scientific use datasets are accessible for scientific research purposes via the Datalab. The Datalab includes R and Python environments where researchers can query the data via SQL queries. WIH OJA microdata cannot be downloaded.
Researchers can request access to WIH OJA scientific use datasets for scientific research purposes via the microdata access portal.
Methodological information on OJA data can be found in the WIH OJA microdata reference metadata. Information on what variables are available and corresponding definitions can be found in the WIH OJA Data Dictionary and Structural Metadata.
